In the Atp-adp Cycle What Is Being Recycled Over and Over Again
Why the body needs nutrient
Your metabolism is the collection of chemical reactions that occur in your cells to sustain life. Some of these reactions apply stored energy to build things up, which we phone call anabolism, while other reactions break things downwardly, releasing free energy that can be stored for futurity use, and this is called catabolism. Imagine that the hamburger you're having for dinner, made of proteins, fats, and carbohydrates, is a collection of lego blocks of various colors and shapes. It took a lot of energy to organize those blocks into that complex structure, and breaking the blocks apart releases that energy and frees the blocks and so that they can exist built back up into new things. Your body does exactly that when you eat your food. Here's a brief video lecture that summarizes this concept.

Living things suspension downwards the three major categories of foods (proteins, fats, and carbohydrates) into their constituent parts, the individual lego blocks, for two reasons. one) Once the nutrient atoms and groups of atoms (molecules) are cleaved downward, they can be congenital dorsum upwards into the specific kinds of things the organism needs, like bone, muscle, peel, pilus, feathers, fur, bark, leaves, etc. ii) Breaking down the nutrient molecules releases the energy that was holding them together, and that released energy is temporarily stored by the prison cell for the re-building process. Each of these food types requires a unlike breakdown process, and nosotros'll look at those afterwards, just the goal is the aforementioned–have the energy that held those food molecules together and release information technology so that information technology can be stored in a form that the prison cell can use subsequently to build what information technology needs. The prison cell has a special kind of molecule for storing that energy, and it'due south called ATP.
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Adenosine_triphosphate

ATP (Adenosine tri-phosphate) is an important molecule found in all living things. Think of it equally the "energy currency" of the cell. If a cell needs to spend energy to attain a job, the ATP molecule splits off 1 of its iii phosphates, condign ADP (Adenosine di-phosphate) + phosphate. The energy holding that phosphate molecule is now released and available to do work for the jail cell. When the prison cell has extra energy (gained from breaking downwardly food that has been consumed or, in the case of plants, made via photosynthesis), it stores that energy past reattaching a free phosphate molecule to ADP, turning it back into ATP. The ATP molecule is just like a rechargeable bombardment. When it'south fully charged, it'southward ATP. When it's run downward, it's ADP. Even so, the battery doesn't get thrown away when it'southward run down–information technology merely gets charged up again.
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Adenosine_diphosphate
ATP ß à ADP + P + free energy
Here'due south what it looks like chemically. Each phosphate is a PO4 (oxygen has a charge of -2 and there are 4 of them, for a full of -8, and P has a charge of +v, then the cyberspace charge on the phosphate group is -3. If costless H atoms, which are +ane, get added to the O atoms that aren't bonded to 2 things, so the internet charge is zero.)
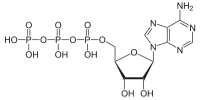
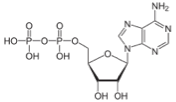
ß à
ATP ADP
In that location are times when the prison cell needs fifty-fifty more energy, and it splits off another phosphate, then information technology goes from ADP, adenoside di-phosphate, to AMP, adenosine mono-phosphate.
ATP ß à ADP + P + energy ß à AMP + P + energy

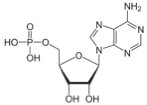
ß à
ADP AMP
In that location are other free energy storage molecules in the cell, like NAD and FAD, but the ATP system is the most common, and the nearly important. Think of the others as different brands of rechargable batteries that do the same job. Adjacent, we'll explore some of the pathways that the body uses to interruption down foods of different types.
What nigh oxygen? Why do we demand that? What happens if y'all put a glass over a candle? Yous starve the burn down of oxygen, and the flame flickers out. If a metabolic reaction is aerobic, it requires oxygen. Buy why? Here's an analogy. Think well-nigh lighting a campfire. What do you need? You demand fuel (the forest), you need heat (it'south harder to light a fire when it's cold), and you need oxygen (because another word for burning is "oxidizing" and, as you might guess, it tin simply occur in the presence of oxygen). Oxidizing something causes it to lose electrons, which ways that energy (the electrons) is released when y'all oxidize, or burn, a fuel. Your nutrient is your fuel. You fire the fuel for energy. You need the oxygen to burn the fuel. This happens in the mitochondria.
jenningssionerve1940.blogspot.com
Source: https://www2.nau.edu/lrm22/lessons/atp/atp.html
0 Response to "In the Atp-adp Cycle What Is Being Recycled Over and Over Again"
Postar um comentário